
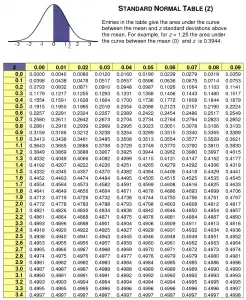
These and other qualities make it a useful tool in statistics and probability calculation of various sorts. The entire distribution density sums to 1 and just like other normal distributions it is fully defined by its first two moments. Similarly, just over 95% of its probability density falls between -2 and +2 standard deviations. For example, 68.27% of values would fall between -1 and 1 standard deviations of a Z distribution. The fact that the distribution is standardized means that the quantiles are known, and that area between any two Z scores is also known. The Z distribution with key quantiles is shown on the graph below: The Z distribution is simply the standard normal distribution of the random variable Z meaning it is a normal distribution with mean 0 and variance and standard deviation equal to 1. Simply select "Z score from P" and enter the p-value threshold in the field to obtain the standard score defining the critical region. The z statistic calculator can also be used in inverse - to obtain a Z critical value corresponding to a given probability. The cumulative probabilities are calculated using the standard normal cumulative distribution function (CDF). The output also contains probabilities calculated for different areas under the standard normal curve which correspond to a one-tailed or two-tailed test of significance. If the variance is known instead, then the standard deviation is simply its square root. The z score calculator can be used to derive a z statistic from a raw score and known or estimated distribution mean and standard deviation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
